Iris Heterochromia
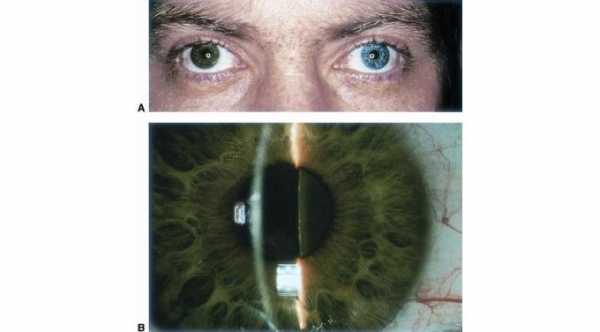
Iris Heterochromia is the difference in the coloration between both iris. It is either hyochromia in which the affected iris is lighter in color than the normal one or hyperchromia in which the affected iris is darker in color than the normal one. There are many causes of this condition and these causes can be divided into congenital and acquired.
Causes of Iris Heterochromia
Congenital causes
1- Hypochromia
Congenital Horner syndrome, Waardenburg syndrome and facial hemiatrophy.
2- Hyperchromia
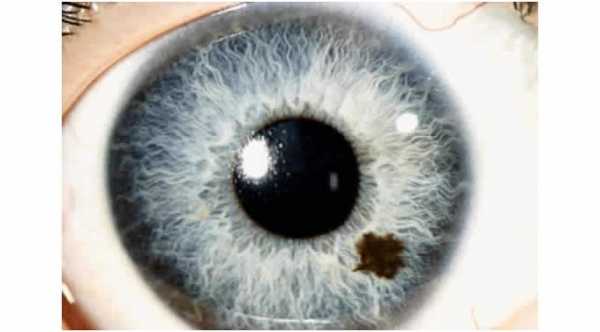
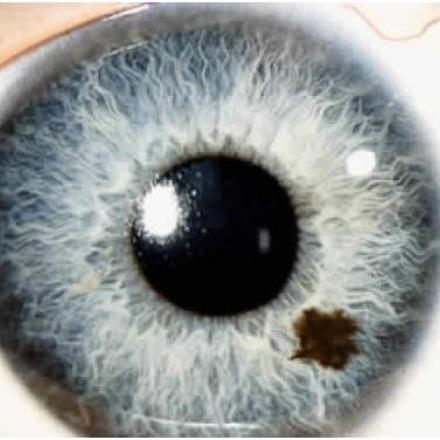
Naevus of Ota (Oculodermal melanocytosis).
Acquired causes
1- Hypochromia
Fuchs heterochromic iridocyclitis, Posner schlossman syndrome, Herpes iritis, pseudoexfoliation syndrome, pigmentary dispersion syndrome, juvenile xanthagranuloma and iris trauma and intraocular surgeries.
2- Hyperchromia
Iris melanoma, iris nevus, Fuchs heterochromic uveitis, siderosis bulbi, Iridocorneal endothelial syndrome and Prostaglandin analogues eye drops such as Xalatan, Lumigan and Travatan.