Blepharospasm | Benign Essential Blepharospasm
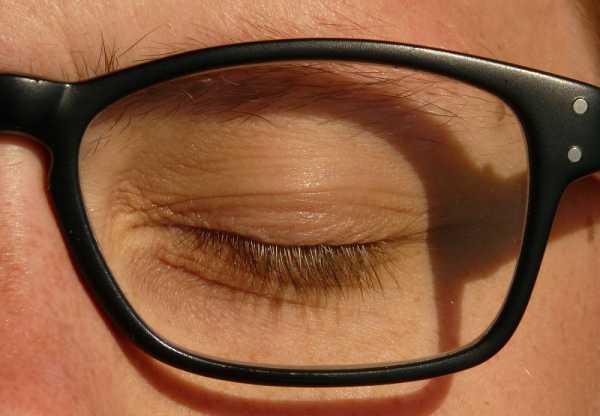
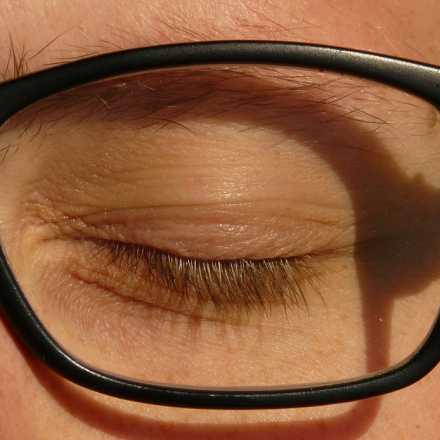
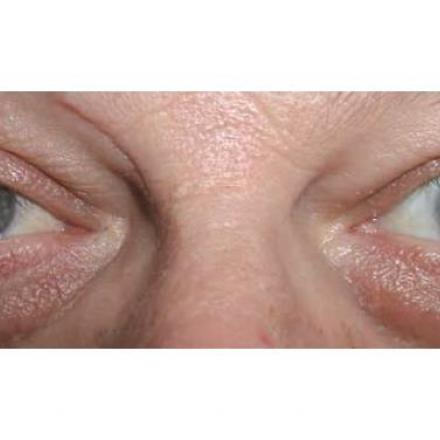
Blepharospasm or benign essential blepharospasm is a bilateral abnormal involuntary contraction of the muscles of the eyelid causing closure of the eyelids. In most severe case, the person can’t open his eyes for few minutes causing functional blindness.
Causes of Blepharospasm
There is no known cause of It but some of the scientists believe there is abnormal function of the basal ganglion. Basal ganglia are responsible for controlling of the muscles. Other scientists believe there is abnormal activity of facial nerve.
What is Hemifacial Spasm
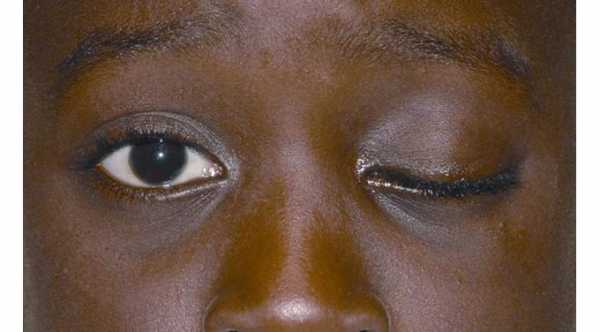
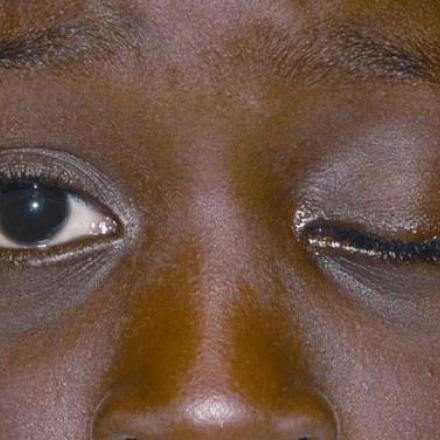
It is similar to Benign essential spasm with involuntary spasms of eyelid muscles but it only occurs in one eye and other muscles of the face on the same side are involved such as the muscles of the cheek and mouth. There are two main causes of it. The first is compression of the facial nerve by blood vessel and the second one is abnormal facial nerve regeneration after trauma.
Reflex Blepharospasm
It is uncontrolled closure of the eyelid due to problem of the eye such as severe dry eyes, corneal abrasion, corneal foreign body and photophobia. Treatment of these cause will cure reflex blepharospasm.
Symptoms of Blepharospasm?
1- Most people will develop it at age 40-60 years and it is more common in female.
2- It is bilateral condition.
3- It can begin without any warning signs.
4- It starts very mild and increases with time gradually.
5- No symptoms during sleeping.
6- Headache and light sensitivity.
7- In severe case can cause complete uncontrolled eyelid closure with functional blindness. It can have negative impacts on the patient’s daily activities.
Blepharospasm and driving
In those patients with mild form of blepharospasm and doesn’t impair their vision, they can drive but in those patients with severe form which makes them functionally blind, they are not allowed to drive.
Risk factors for Blepharospasm
• Family history of tremor or dystonia.
• Bright lights.
• Trauma to the head or face.
• Fatigue, stress and caffeine.
• Some medications that are used to treat psychosis and Parkinson’s can cause it.
Differential diagnosis
1- Hemifacial Spasm.
2- Reflex Blepharospasm.
3- Eyelid myokymia.
4- Stroke that causes meningeal irritation.
5- Tardive dyskinesia which is uncontrolled spasms of the muscles of the eye, face and limbs due to the side effects of antipsychotic medications.
6- Meige syndrome. Neurological disorder with abnormal uncontrolled contractions of the muscles of the eyelid, tongue and jaw.
7- Cerebral palsy.
8- Tourette syndrome.
9- Brain injury.
10- Diseases of the brainstem and basal ganglia such as Parkinson's, Wilson's, Huntington's and progressive external ophthalmoplegia.
11- viral encephalitis.
12- Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis.
13- Jakob-Creutzfeldt disease.
14- Tetanus
Medical Treatment of Blepharospasm
1- Treatment of the causes of reflex blepharospasm such as treatment of dry eyes and blepharitis.
2- Patients with light sensitivity can wear sunglasses tinted with rose-colored FL-41 to reduce reflex blepharospasm from bright lights.
3- Injection of botox or botulinum toxin A to the muscles of the eyelid protractor muscles that are responsible for the blepharospasm such as orbicularis oculi, procerus muscles and corrugator supercilia. This injection should be given every 4-6 month and over 90% of the patients improve with it. The injection starts to have an effect on the spasms after 2-4 days and the peak effects at 7-10 days.
Surgical treatment of Blepharospasm
The first line of treatment is always medical but in some cases who no longer response to botox injection, surgical treatment is the second option.
Types:
1- Surgical avulsion of facial nerve. Facial nerve innervates eyelid muscles, so ablation of this nerve helps to reduce or prevent spasm of eyelid. This procedure has high recurrence rate.
2- Surgical myectomy of orbicularis and protractor muscles can give long relief from blepharospasm.