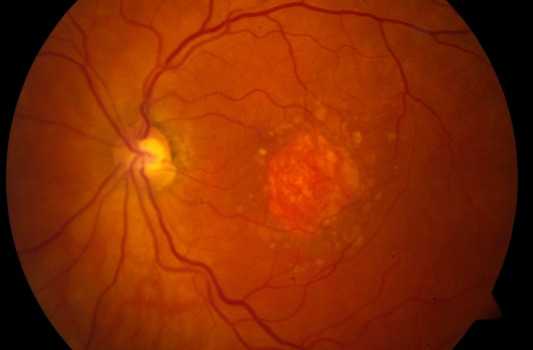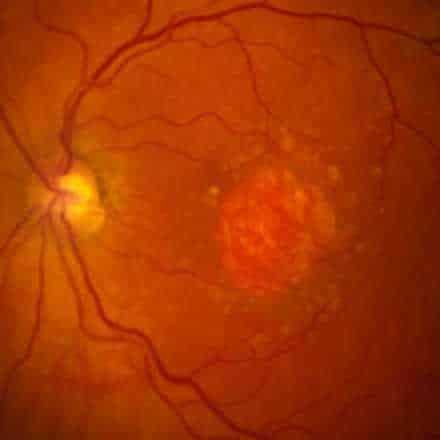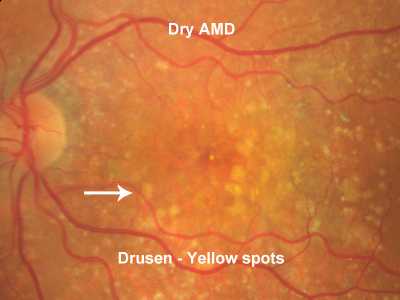
Drusens
Multiple small yellow to white lesions that are located within the Bruchs membrane. Bruchs membrane lies between the Retinal Pigment Epithelial layer and the choriocapillaries layer of the choroid. They are seen most commonly in older patients with Age Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) but also can be seen in young people.
Types of Drusens
1- Small Hard Drusens
Well defined small lesions with sharp discrete borders. The size is less than 63 um. They are localized accumulation of hyaline material in the Bruchs membrane The presence of this type of drusen alone is not enough to make the diagnosis of Age related macular degeneration.
2- Large Soft Drusens
Drusens with the size of more than 63 um and with ill defined border. The presence of this type of drusen will increase the risk of choroidal neovascularization and Wet Macular Degeneration. Coalescence of large areas of soft drusen will cause detachment of Retinal Pigment Epithelial layer.
3- Basal Laminar Drusens
Yellowish nodules that located between the basal lamina of the RPE and the inner collagenous layer of Bruch's membrane.
Risk factors to develop Age Related Macular Degeneration in patients with drusens:
1- Old age.
2- Soft Drusens.
3- Decreased Vision.
4- Hypo or hyperpigmentation of Retinal Pigment Epithelial cells
5- Fellow eye or the other eye that already developed Age-Related Macular Degeneration.