Phacomorphic Glaucoma
Phacomorphic Glaucoma is acute angle closure glaucoma that is induced by intumescent cataract which is abnormally large in size.
This type of cataract can be seen in elderly people especially in areas with limited access to ophthalmic care. Also we can see this type of cataract after trauma.
Normally the natural lens will increase in size with age in anteroposterior dimension and it will become in close contact to the iris which lies infront of it.
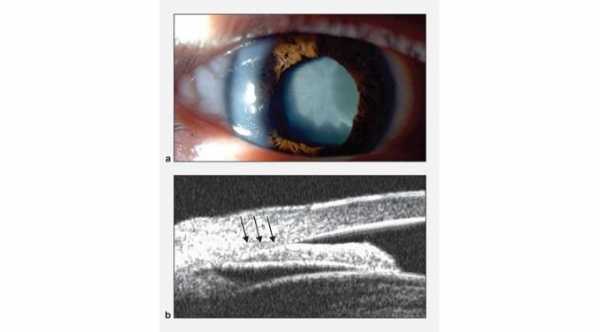
With cataract overgrowth, the space between the lens and the iris will decrease and this will affect the aqueous humor outflow from the posterior chamber to the anterior chamber leading to iridolenticular contact and pupillary block.
With pupillary block there will be positive pressure gradient between the posterior and the anterior chamber causing high intraocular pressure. Also with this positive gradient, there will be anterior displacement of lens-iris diaphragm causing closure of the angle by the peripheral part of the iris. This is more likely to occur in patients with short axial length of the eye like in hyperopia.
Signs and Symptoms of phacomorphic Glaucoma
Symptoms
Same as symptoms of Acute Angle Closure Glaucoma
Signs
1- Red eye.
2- Corneal edema.
3- Shallow anterior chamber.
4- High Intraocular pressure.
5- Narrow angle.
6- Iris bombé, in which the iris is bulged anteriorly in the anterior chamber.
Treatments of Phacomorphic Glaucoma
Initial therapy for this condition consists of anti glaucoma eye drops to decrease the intraocular pressure and the definitive treatment will be with cataracts surgery and Intraocular lens insertion plus surgical or laser Iridotomy.