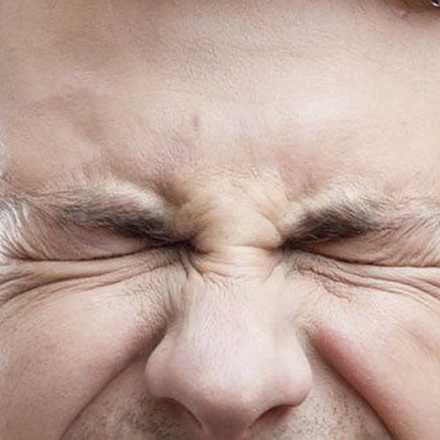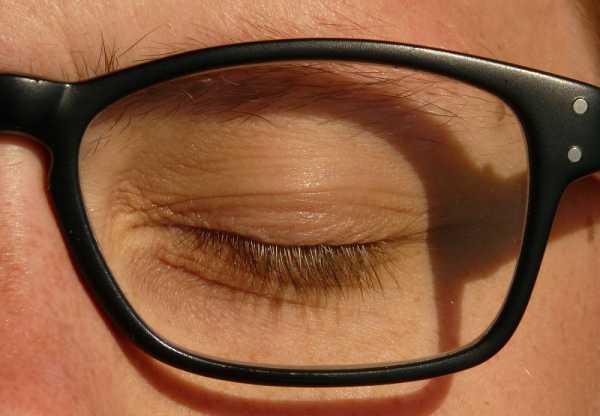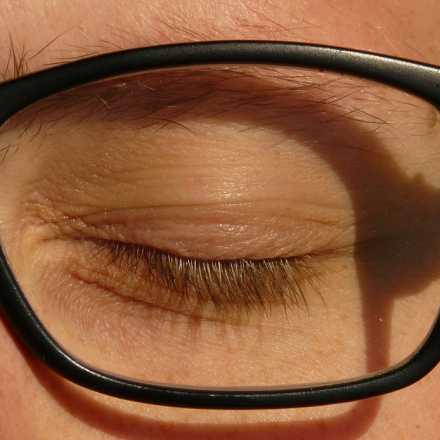
Causes of ptosis can be divided into five categories
1- Myogenic causes
Myogenic means abnormalities in the muscles that control the movements of the eyelid. The main muscle of the upper eyelid is Levator muscle. Diseases that cause myogenic abnormalities are: Myasthenia Gravis, Myotonic dystrophy, progressive external ophthalmoplegia, ocular myopathy and oculopharngeal dystrophy.
2- Mechanical Ptosis
The weight of the upper eyelid is larger than normal due to mass effect of the tumor or due to scarring of the eyelid. Another common cause these days is retained contact lens under the upper eyelid.
3- Neurogenic Causes
There are problems in the nerves that supply the eyelid and its muscles. Levator muscle of the eyelid is supplied by Third cranial nerve which is called Oculomotor nerve. Lesions to this nerve can cause eye ptosis. A small muscle in the upper eyelid called Muller muscle and it is supplied by sympathetic innervation.
horner's syndrome is caused by a defect in the sympathetic innervations and ptosis can occur. Another cause of Neurogenic is Marcus Gunn jaw winking syndrome in which there is aberrant innervation of the levator muscle.
4- Aponeurotic causes
Levator muscle divided into two parts, the muscle and the aponeurosis which is like a fascia or a thin tendon. Disinsertion or dehiscence in the levator aponeutosis can cause ptosis. Causes of it are old age, previous eyelid surgery, trauma, chronic upper eyelid edema and blepharochalasis.
5- Congenital causes
There is poor levator function from birth in which there is fibrosis of the levator muscle. Congenital Horner syndrome and birth trauma can cause it.