Central Serous Retinopathy
Central serous retinopathy or Central serous choroidopathy is characterized by detachment of neurosensory layers of the retina from the underlying layers of retinal pigment epithelium at the macular area.
It occurs due to defects in the Retinal Pigment Epithelial cells. The space between the detached neurosensory retina and the underlying retinal pigment epithelial layer is occupied by a clear serous fluid but sometimes can be turbid and yellowish in color.
Causes and Risk Factors of Central Serous Retinopathy
The main cause of this disease is unknown but they found multiple risk factors associated with it and these risk factors are:
1- Type A personality.
2- Emotional Stress.
3- Gastro-esophageal Reflux.
4- Systemic Lupus Erythematous.
5- Tobacco use.
6- Alcohol use.
7- Systemic hypertension.
8- Organ Transplantation.
9- Corticosteroid which can be either oral, intravenous or through inhalation.
Central Serous Retinopathy Symptoms
1- Unilateral Eye
Usually the condition is unilateral or occurs in one eye.
2- Blurred vision
That can be improved with plus lens because the retina is pushed forward and the eye becomes hyperopia or farsighted.
3- Metamorphopsia
Distorted lines or images.
4- Micropsia
Images look smaller than the actual size of it.
5- Dark adaptation
Impaired dark adaptation and delayed retinal recovery time to bright light.
6- Reduce contrast sensitivity and color vision
Diagnosis of Central Serous Retinopathy
1- Slit Lamp Examination
Transparent retinal swelling in the posterior pole over the macular area.
2- Fluorescein Angiography
The diagnosis can be confirmed by this test in which a special pattern of dye leakage under the retina can be seen. This diagnostic test is very helpful in treatment because the sites of leakage can be treated with laser.
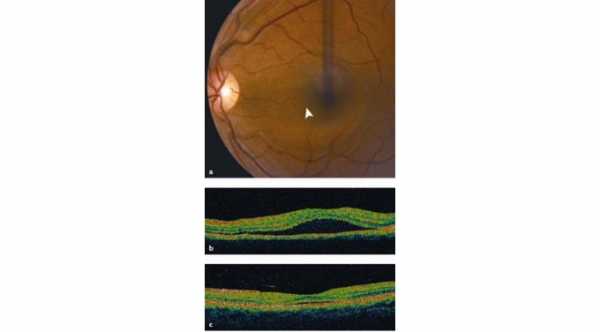
3- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Shows the detached retina from the underlying layer. This diagnostic test can also be used in the follow up visits to determine the level of improvement.
Central Serous Retinopathy Treatment
Most patients have a spontaneous recovery within three to six months but in some patients it can last for more than 1 year especially in elderly.
The first line of treatment is observation. If the patient shows no signs of improvement after 4 months, laser photocoagulation can be used to treat sites of fluorescein leakage. Other indications of laser treatments are permanent changes from Central serous retinopathy in the other eye, multiple recurrences or the patient requires faster recovery due to work.
This treatment is done only for leakage sites that are away from the fovea. Laser Argon Photocoagulation treatment helps to reduce the duration of the disease and helps to reduce the incidence of recurrence but has no effects on the final visual outcomes.
For leakage sites at or near the fovea, the treatment can be done by Photodynamic treatment (PDT).
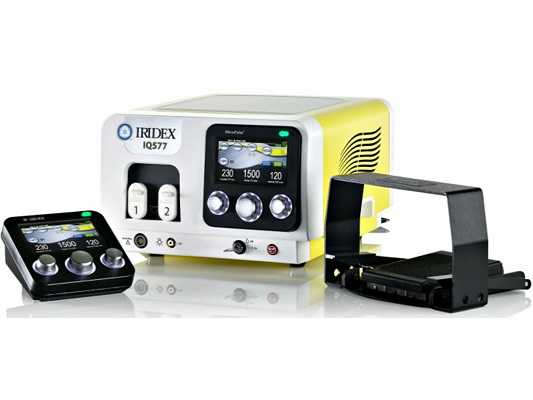
There is a new Laser Treatment with IRIDEX MicroPulse. Read more Iridex Micropulse Laser
Treatment with Anti-VEGF can also be used as an option but still under study.