How Diabetes Affects Your Vision
You’ve probably heard some variation of this sentiment that “Health is the most important thing in your life.” You’re probably also familiar with this gem: “You don’t know what you have until it’s gone.” Sadly, when it comes to our well-being, there is a lot of truth to that. Many don’t appreciate their health until it has been compromised.
According to the CDC, 60 percent of adults in the U.S. have a chronic disease and 40 percent are suffering from two or more diseases. Of the leading causes of death and disability, diabetes ranks sixth, after heart disease, cancer, lung disease, stroke, and Alzheimer’s.
What is diabetes? How does it affect your vision, and what are some precautions you can take to prevent or manage it?
What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes is an illness that results in insulin resistance, which simply means that your body has trouble processing food to use as energy. For your body to function as it should, your food is converted into glucose and requires a hormone called insulin to be able to use that glucose as energy. When someone has diabetes, their body is unable to produce enough insulin, or it produces too much, which leads to increased levels of stored glucose in your blood.
The Three Types of Diabetes
1. Prediabetes: Your glucose tolerance has been impaired but not completely compromised yet. Prediabetes blood sugar levels can be likened to those found in people who are fasting, which is between 100 and 125 mg/dl.
2. Type 1 Diabetes: Also known as “insulin dependent” diabetes, Type 1 is an autoimmune disease that typically affects people under the age of 20. The immune system destroys insulin-producing cells, which is why the body becomes dependent on insulin supplements.
3. Type 2 Diabetes: Also known as “non-insulin dependent” diabetes. Type 2 is by far the most common type of diabetes. Your body can produce insulin; in fact, it produces too much of it and is unable to use it efficiently.
While the number of people living with diabetes is high, the number at risk of developing the disease is even higher. Nearly three times as many people have the early signs of diabetes — commonly known as pre-diabetes — and likely will develop the disease if they do not make lifestyle changes.
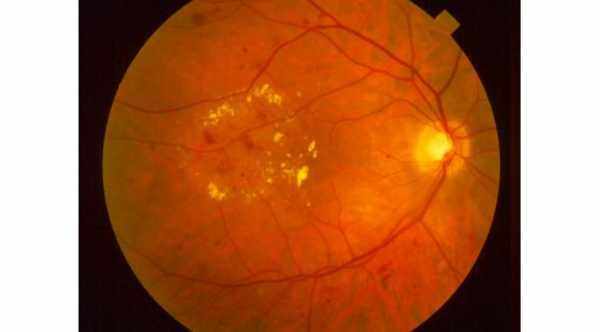
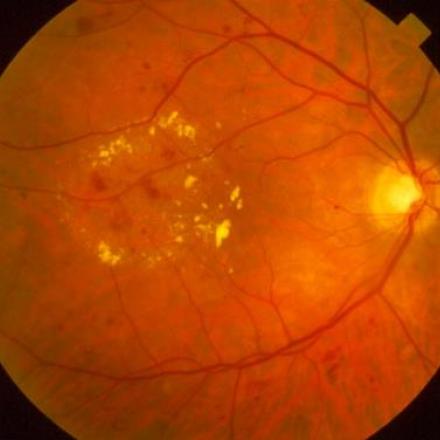
How Does Diabetes Affect Your Vision?
There are both short-term and long-term complications that can affect the eyesight of people with diabetes.
● Long-term effects: When diabetes is not controlled, this can lead to high blood sugar levels that damage blood vessels, which can then damage the retina and lead to blurred vision.
● Short-term effects: The results are the same (blurred vision), but the reasons are different. In the short term, it’s caused by fluid moving in and out of the eyes from high blood sugar, causing the lens of the eyes to swell.
Diabetes-related eye problems are progressive and will worsen with time if the diabetes is left untreated. These issues can take several years to develop.
In the worst-case scenario, the retina can become detached, and the person may lose sight in one or both eyes. At this point, the patient will only be able to distinguish light from dark. Glaucoma is another concern for those with diabetes.
Glaucoma is caused by the build-up of pressure in the eye that affects the main nerve traveling from the eye to the brain. This can result in blurred vision, tunnel vision, and even vision loss if untreated.
For contact wearers, there is a new technology that allows contact lenses to measure glucose levels, thereby letting you know in real time whether or not your body is having trouble managing glucose levels ― a sign of developing diabetes.
Precautions You Can Take
If you have diabetes and are using medication to treat it, it’s vital to use your diabetes medications safely. Diabetes medications have advanced dramatically over the years and can help prevent vision problems, as long as they’re taken as prescribed.
Further, take a look at your diet. Diabetes is often the result of too much junk food over a long period of time. Often, these negative choices are the result of misconceptions, such as the idea that junk food is a cheaper alternative to nutritious foods. If you’re interested in trying to reverse your diabetes, consider doing so naturally through an improved diet. Try the following dietary changes:
Foods to Remove From Your Diet
● Refined sugar
● Dairy products
● Grains
● Alcohol
● Genetically modified foods
● Hydrogenated vegetable oils
Foods to Add to Your Diet
● Foods high in fiber
● Chromium-rich foods
● Magnesium-rich foods
● Healthy fats
● Good sources of protein
● Low-glycemic foods
If you have prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, eating foods that are low on the glycemic index is especially important, as high-glycemic foods will convert to sugar too quickly for your body to handle and contribute to your problems rather than help solve them.
If you think diabetes may be the root of your health problems, it’s important to see a doctor for a checkup and blood tests, and then take the necessary steps to controlling or reversing the disease, should you have it.
Remember, when you have good health, you have everything. It’s not the kind of thing you want to miss once it’s gone.