Ptosis Definition
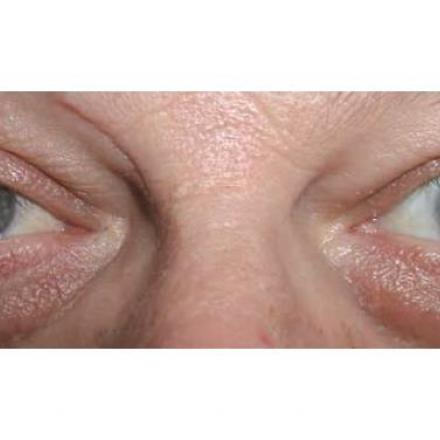
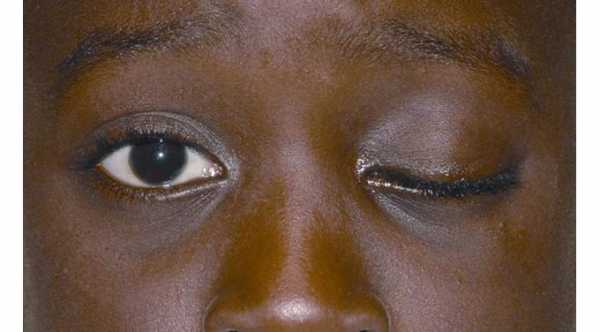
Eye ptosis or Blepharoptosis means abnormally drooping of the upper eyelid. Although lower eyelid ptosis can also occur in which the margin of the lower eyelid is abnormally low.
Normally the margin of the upper eyelid should be about 2 mm below the limbus (area between the cornea and the limbus), while the margin of the lower eyelid should be at the level of the limbus.
Ptosis causes
Can be divided into five categories which are:
1- Myogenic Ptosis
2- Mechanical Ptosis
3- Neurogenic Ptosis
4- Aponeurotic Ptosis
5- Congenital Ptosis
Read Full article about Causes of ptosis
Pseudoptosis
It is a false impression of the droopy eyelid in which there is no defects in the upper eyelid or the function of the muscle and nerve. Treatment of these defects will resolve ptosis.
There are causes of the tissue that surround the eyelid and these causes are:
1- Decrease in the orbit volume. Microphthalmia (small eyeball), enophthalmia (inward deviation of the eyeball) and artificial eye can cause Pseudoptosis due to lack of support.
2- Lid retraction of the other eye. Retraction of the upper eyelid in the other eye can ptosis.
3- Proptosis of the other eye.
4- Hypotropia of the same eye. The eyelid usually follows the eyeball. Hypotropia means downward deviation of the eyeball and in this case the upper eyelid will follow it downward.
5- Brow Ptosis. The upper eye lid is also connected to the brow muscles and when there is ptosis of brow muscles, there will be also drooping of the upper eyelid.
6- Dermatochalasis. Which means excessive skin in the upper eyelid. It can be like a mechanical cause of ptosis.