Horner Syndrome
Horner Syndrome is a disease that occurs due to damage of sympathetic supply of the pupil, eye lid and skin. The causes of it are divided according to the site of the damage to the sympathetic pathway. There are three main sites which are called central, preganglionic and post ganglionic.
Central Causes of Horner Syndrome
These causes can occur to sympathetic nerve pathway from the brain to the spinal cord at the level of cervical vertebra number 8 to thoracic vertebra number 2.
1- Stroke.
2- Tumor.
3- Head and neck trauma.
Pre-ganglionic Causes
Which can occur to sympathetic nerve pathway from the spinal cord to cervical ganglia.
1- Pancoast tumor. This tumor occurs in the upper part of the lung.
2- Rib fracture.
3- Neck trauma or surgery such as thyroid surgeries.
Post-ganglionic Causes
Which can occur to sympathetic nerve pathway from cervical ganglia to the eye. This part pass through nerves along the carotid artery.
1- Carotid dissection or aneurysm which can be life threatening condition and should be diagnosed when horner syndrome associated with pain in the neck.
2- Neck trauma and surgeries.
3- Cavernous sinus lesions. Because carotid artery along with sympathetic nerves will pass through this sinus.
Signs and Symptoms of Horner Syndrome
The symptoms of it will depend mainly on the cause. Three things are helpful for the diagnosis of it. These things are:
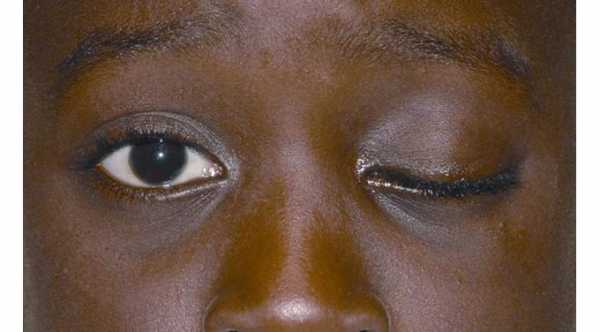
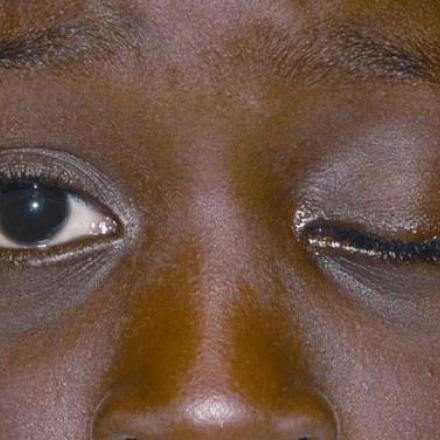
1- Miosis. The affected pupil will be small and constricted with poorly reactive to light. This will cause anisocoria which is inequality in the size of pupil of both eyes.
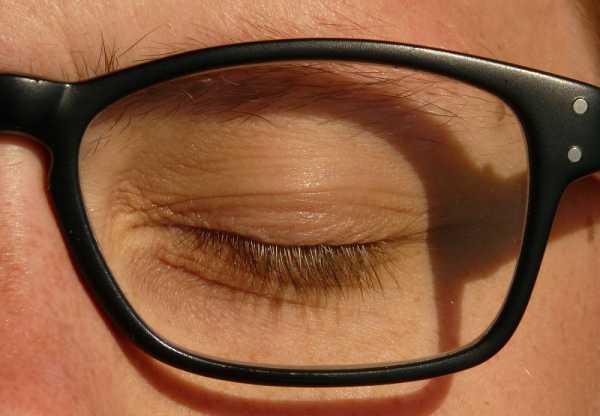
2- Ptosis which is drooping of the upper eyelid while Reverse Ptosis which is lower eyelid elevation.
3- Anhidrosis. Which is loss or lack of sweating in the affected side of face and forehead. This sign usually indicates pre ganglionic lesions.
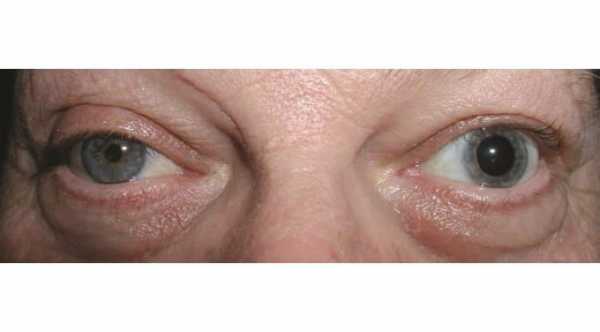
4- In longstanding or congenital horner symdrome there will be iris heterochromia which is a difference in the color of both iris. The affected iris usually will be lighter than the normal one.
5- Enophthalmos. Which is sunken of eyeball.
Diagnosis of Horner Syndrome
Through pharmacological tests, we can diagnose and also localize the site of the lesions. We will use medications such as Topical cocaine and topical hydroxyamphetamine for diagnosis. Imaging tests such as MRI and CT scan for the bran, neck, spin and lung should also be done.
Treatments of Horner syndrome
1- Treatments should be focused mainly on the cause of it.
2- After the cause is treated and the patient is stable, we can consider Ptosis surgery treatment.