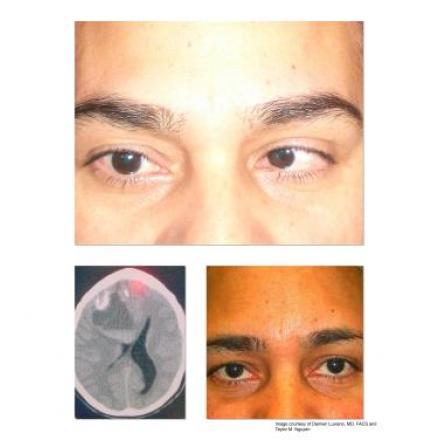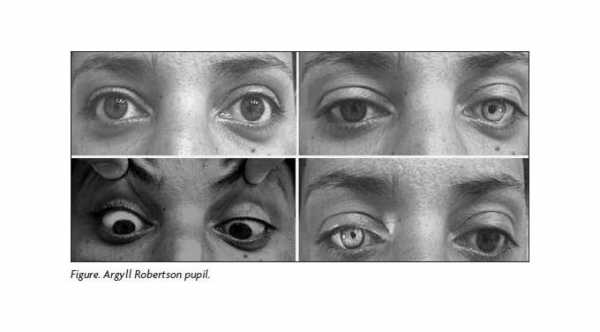
Argyll Robertson Pupil
Argyll Robertson Pupil is a clinical condition that affects both pupil and it is caused by lesions to dorsal midbrain (Pretectal nucleus and interneurons that connect to Edinger Westphal Nucleus). The pupil is miosed or small and not reactive to light but it reacts to accommodation or near reflex. This condition is called light near dissociation.
The main cause of this condition is Neurosyphilis or stage 3 syphilis. Other causes are Diabetes Mellitus, Multiple sclerosis, trauma and aberrant regeneration of 3rd cranial nerve (Oculomotor Nerve).
Login or sign up to comment