Ophthalmology Terminology F
Facial nerve palsy. Paralysis of the seventh cranial nerve. This nerve
supplies facial muscles and eyelid muscles.
Farnsworth-munsell test. High effective test that is used to measure color vision and detect any defects in color vision.
Fenretinide
Filtering Shunts in Glaucoma. Small devices or instruments that is used in glaucoma patients in order to drain aqueous humor from the anterior chamber to extraocular space between the conjunctiva and sclera. It is implanted on the sclera and under the conjunctiva.
Five-Fluorouracil. Anti-metabolites medication that is used in trabeculectomy glaucoma surgery in order to inhibit the formation of fibrosis.
Flecked Retina Syndrome. Group of retinal dystrophies which are characterized by formation of small, yellow to white lesions in the retina that can extend all over the retina.
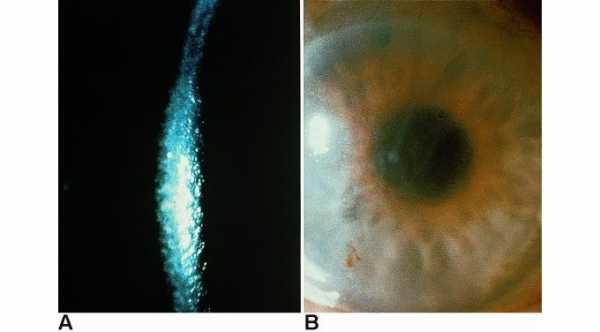
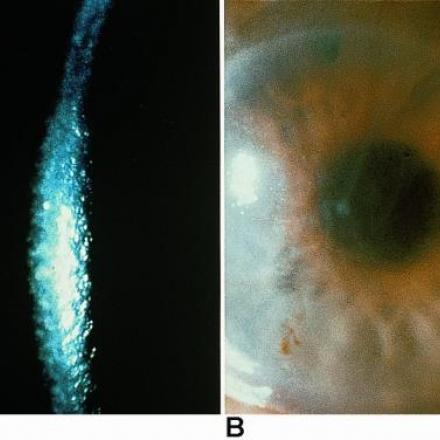
Fleischer Ring. A sign that occurs in keratoconus in which iron deposition occurs in the epithelial layer of the cornea. It surrounds that base of the cone.
Floaters
Fovea centralis. It is part of the eye that is located in the center of the macular area of the retina. It is responsible for the sharp central vision.
Foville Syndrome. Lesion to the dorsal Pons due to vascular diseases or tumors and it is characterized by involvement of fifth and eighth cranial nerves plus central sympathetic fibers which will lead to Horner syndrome.
Frey Syndrome. Abnormal regeneration of ninth cranial nerve in which abnormal connections between salivation fibers and sympathetic fibers occur. This will lead to flushing and sweating when person eat.
Frisby Plate. Special plates that are used to test for Three dimensional abilities in binocular single vision.
Fuchs Endothelial Dystrophy. Bilateral corneal dystrophy which affects the endothelial cells of the cornea. It will lead to persistent stromal edema, epithelial edema and bullous keratopathy.
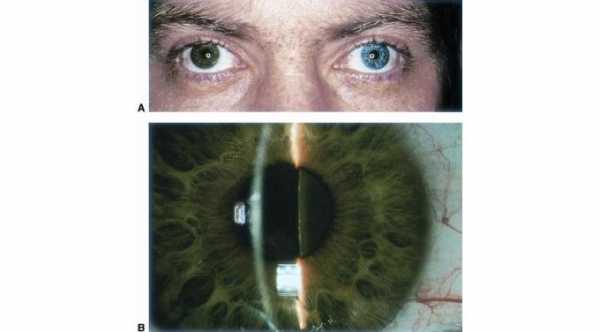
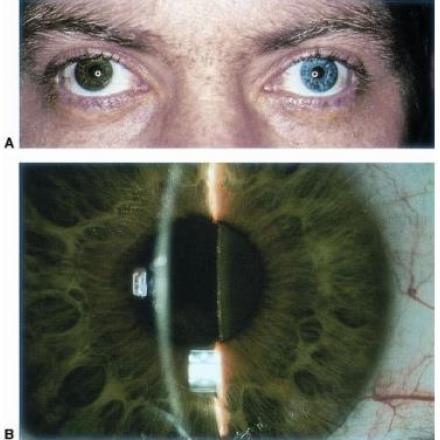
Fuchs Heterochromic Iridocyclitis. Idiopathic type of anterior uveitis that causes iris atrophy, cataract and glaucoma. iris atrophy can make the eye appeared lighter in color than the other eye.
Fundus Albipunctatus. Type of hereditary night blindness syndrome with abnormalities in visual pigments.Patient has slow dark adaptation.
Fundus Flavimaculatus. Group of macular dystrophies with abnormal yellow to white lesions in the retina.
Fungal Keratitis. Infection of the cornea by fungus.