Ophthalmology Terminology M
Macropsia. Increase in the image size that is perceived by the brain due to crowding of the foveal cones.
Macula. Part of the retina which lies between two major branches of retinal vessels and are responsible for the central visual acuity. Macula contains the fovea which is responsible for the highest central visual acuity.
Macular Corneal Dystrophy. Type of corneal dystrophy that occurs in both eyes due to deposition of mucopolysaccharides in the stromal layer of cornea.Cornea is opaque and the patients may requires corneal transplantation early.
Macular Edema
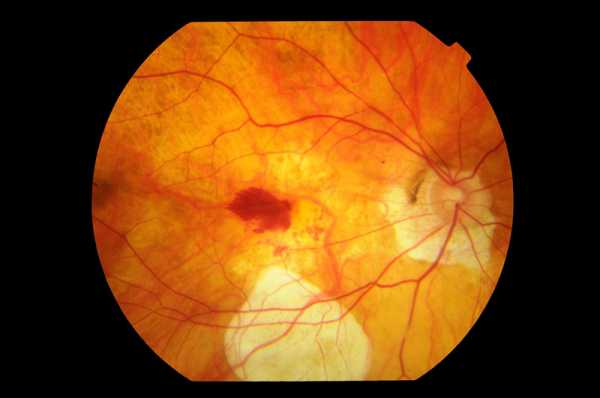
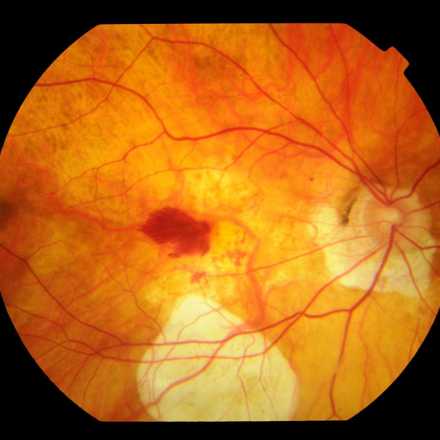
Macular Hole. A hole that occurs in the neurosensory layer of the retina. It has stages that depends on the thickness and the presence of posterior vitreous detachment.
Macular Pucker. Abnormal membrane that is formed over the macular area.This membrane contracts over the macula, causing macular striae.It is the same as epiretinal membrane except that there is contraction of the membrane.
Madarosis
Maddox Rod. A test that can be used to measure heterophoria by dissociates the eyes for far vision.
Maddox Wing. A test that can be used to measure heterophoria by dissociates the eyes for near vision.
Malignant Glaucoma
Marcus Gunn Jaw Winking Syndrome. A common cause of Ptosis in which there is innervation of the eyelid muscle and jaw muscle with the same nerve innervation.Movement of Jaw will cause retraction of the eyelid muscle.
Marfan Syndrome. Systemic connective tissue disorder that occurs due to defects in collagen fibers.It has ocular manifestations and systemic manifestations. Ocular manifestations such as subluxated lens,glaucoma and retinal detachment.
Meesmann’s Syndrome. Type of corneal dystrophy that affects the epithelial layer of the cornea.It is characterized by small tiny epithelial cysts of the cornea with photophobia.
Megalocornea. Large corneal diameter but with normal length of the eye, clear cornea and normal intraocular pressure.
Melanosis, Conjunctiva. Pigmentation of the conjunctiva in the limbal and interpalpebral region.
Meibomianitis. Inflammation of the Meibomian Gland of the eyelid.
Metamorphopsia. Abnormal vision in which the patient sees distortion in the shape or size of the object.
Microcornea. Small corneal diameter that is associated with other ocular abnormalities such as shallow anterior chamber, glaucoma, cataract and optic nerve hypoplasia.
Microcystic Corneal Dystrophy. Type of corneal dystrophy that affects the epithelial layer of the cornea. It is characterized by recurrent corneal erosion and diffuse tiny cysts.
Micropsia. Decrease in the image size that is perceived by the brain due to separation of foveal cones.
Millard Gublar Syndrome. A condition that occurs due to lesion of the fasciculus part of the sixth cranial nerve(Abducens) as it passes over the pyramidal tract. It characterized by paralysis of the sixth cranial nerve in the same side as the side of the lesion and contralateral muscle weakness of the body.
Mitomycin C. Natural alkylating agent that is one of the anti-metabolites medications. It prevents fibrosis by cross-linking with DNA strands and inhibits fibroblast cells.
Monofixation Syndrome. Abnormalities of the binocular vision with small squint angle.The deviated eye has central scotoma but the patient can form binocular vision with his peripheral vision.
Mooren’s Ulcer. A condition with peripheral corneal ulceration with severe pain, redness and epithelial defects. It has the risk of corneal perforation.
Multifocal Choroiditis. A condition with Mutifocal spots or areas of choroidal inflammation that are associated with inflammation of the vitreous body (Vitritis).
Multiple Evanescent White Dot Syndrome. A condition with idiopathic posterior uveitis that occurs in young female. It is unilateral self-limited condition with sudden onset decreased vision and optic disc swelling.The prognosis is excellent and most of the time no treatment is required.
Myasthenia Gravis. Auto-immune disease that is characterized by muscle weakness that worsen with activities and improves with rest.
Myopia. Type of the refractive error of the eye in which the light rays that entered inside the eye are focused in a point infront of the retina. It is also called nearsightedness. The patient can see the near object clearly but the far objects are blurred.
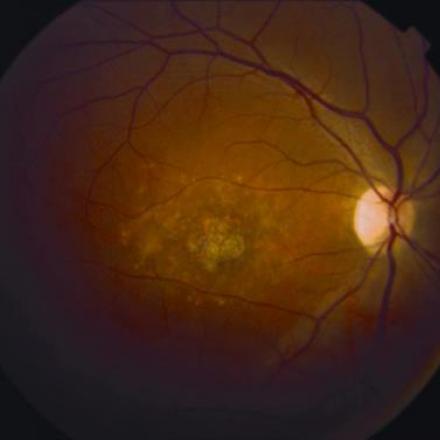
Myopic Macular Degeneration. Myopic Macular Degeneration is a condition with excessive myopia with progressive expansion of the eye that is associated with formation of posterior staphyloma and severely blinding complications of the macula.