Birdshot Chorioretinopathy
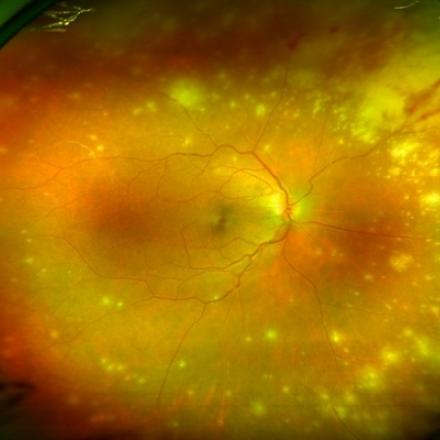
Birdshot Chorioretinopathy is uncommon chronic form of posterior uveitis with multiple clinical exacerbation.It is characterized by Vitritis (Inflammation of the vitreous body) and multiple hypopigmented spots of the choroid that are concentrated mainly in the posterior pole of the fundus.
Etiology of Birdshot Chorioretinopathy
The main cause of birdshot retinochoroidopathy is unknown but autoimmune element is suspected. There is lymphocytic response against S-antigen and interstitial retinoid binding protein. These two antigen are found in photoreceptor cells of the retina. This disease has the strongest HLA association in which 96% of patients with this disease have positive HLA-A29.
Pathophysiology
Focal Lymphocytic (CD8 T-cells) infiltration of the choroid and choroidal blood vessels and mild retinal infiltration.
Symptoms of Birdshot Retinochoroidopathy
Birdshot Retinochoroidopathy is typically bilateral but asymmetric. The most common symptoms are blurred of vision and Floaters.
Other common symptoms
1- Nyctalopia. Decrease night vision.
2- Dyschromatopsia. Defect in color vision.
3- Metamorphopsia. Distorted vision in which straight lines appear as wavy lines.
4- Glare and photophopia.
5- Decrease in peripheral vision.
Signs of Birdshot Chorioretinopathy
1- Small orange to yellow colored spots at the level of outer retinal layer, retinal pigment epithelial layer and inner choroid that are concentrated mainly in the inferior and nasal side of the posterior pole and mid peripheral part of the retina.
2- Mild to moderate Vitritis which is inflammation of the vitreous body.
3- Mild anterior chamber uveitis.
4- Retinal vasculitis and optic disc edema. In chronic form there will be attenuated retinal blood vessels and optic disc atrophy.
5- Cystoid macular edema.
6- Subretinal and choroidal neovascularization can occur in chronic disease.
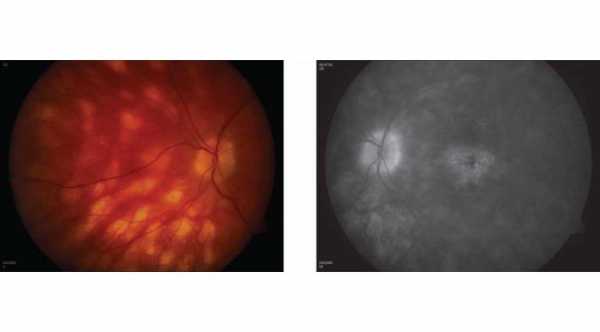
7- In fluorescein angiography. Early minimal Hyperfluorescence of the birdshot spots with late staining.
Treatment of Birdshot Chorioretinopathy
1- Corticosteroid which can be given orally and/or periocular injection
2- Immunosuppressive medications such as cyclosporine.