Periorbital Cellulitis
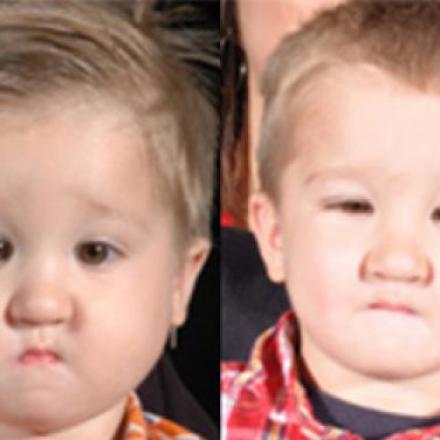
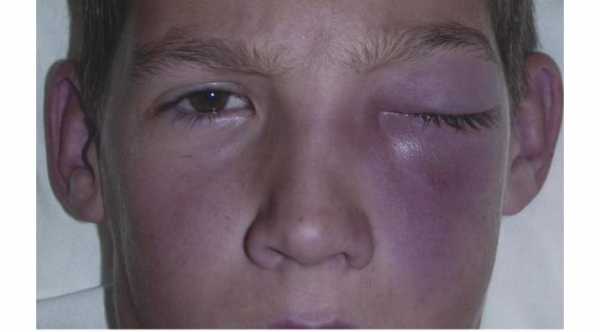
Periorbital cellulitis is the infection of the tissues that surrounds the eye. The globe itself is intact.The infection is confined to the area that lies infront of the orbital septum. Usually it involves one eye but sometimes both eyes can be affected.
What are the causes of Periorbital Cellulitis?
The most common cause is bacterial infection of the surrounding tissue. The most common bacteria are same as those bacteria that cause upper respiratory Tract infection such as staphylococcus (aureus, epidermidis) and streptococcus.
Haemophilus influenza was the most common cause of bacterial infection especially in children under 6 years but was dramatically decrease after 1985 with the introduction of H influenza type b vaccine (Hib).
This bacterial infection reached the Periorbital tissue from adjacent tissue, such as:
1- Infection of the eyelid. Such as from untreated eye stye and chalazion.
2- Infected wound of the eyelid.
3- Upper respiratory tract infection and paranasal sinusitis.
4- Dacryocystitis or infection of nasolacrimal sac and duct.
5- Dacryoadenitis or infection of lacrimal gland.
7- Oral Procedures.
Age
More than 80% of Periorbital cellulitis occurs under the age of 10 years.
Periorbital Cellulitis Symptoms and Signs
1- Pain and tenderness of the surrounding tissue with mild pain associated with eye movements.
2- Mild to moderate fever.
3- Conjunctivitis and red eye.
4- Excessive lacrimation and Epiphora.
5- Eye discharge.
6- Swelling of the Periorbital tissue and eyelid which can range from mild to severe.
7- Redness of the skin and the surrounding tissue.
8- Blurred vision.
Diagnosis of Periorbital Cellulitis
1- Full ocular examination to determine the primary site of infection.
2- Samples from conjunctival discharge, eyelid lesions and samples from nasolacrimal ducts.
3- Blood culture tend to be negative in most of the cases.
Differential Diagnosis of Periorbital Cellulitis
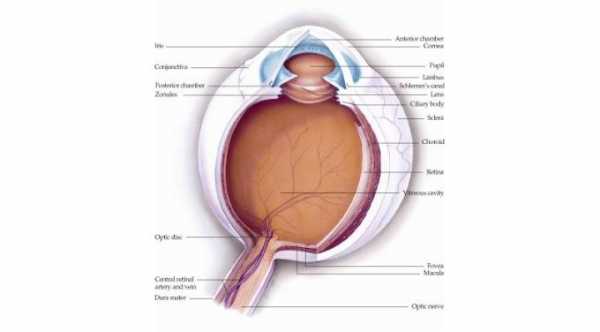
1- Orbital Cellulitis.This is the most important differential diagnosis.This is a serious condition and has a higher morbidity than periorbital cellulitis. Periorbital cellulitis confined to the area of the eyelid that lies in front of orbital septum while orbital cellulitis lies deep to this septum and spread directly to the tissue that surrounds the eye including extraocular muscles.This condition required more aggressive treatment with antibiotics and sometimes may require surgical drainage of abscess.
2- Viral and Bacterial conjunctivitis.
3- Inflammation and infection of lacrimal gland and nasolacrimal ducts.
4- Other causes of red eyes such as allergic conjunctivitis, scleritis and uveitis.
Periorbital Cellulitis Treatment
1- Most of the cases can be treated as outpatient and no hospital admission is required unless young child with severe condition.
2- Antibiotics in the form of eye drops is required in mild cases.
3- Moderate and severe cases require systemic antibiotics such as oral and intravenous antibiotics.
4- Improvement of the condition should be noticed within 24-48 hours. Failure of improvement can be a sign of abscess formation which require drainage or transformation to orbital cellulitis which requires hospital admission with more aggressive investigation and treatment.