Hydrus Microstent For Glaucoma
Hydrus Microstent is the first “intracanalicular scaffold” developed for the treatment of Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma (POAG). It is amicroinvasive glaucoma surgical (MIGS) device designed to address the high intraocular pressure (IOP) that manifests in patients suffering from POAG.
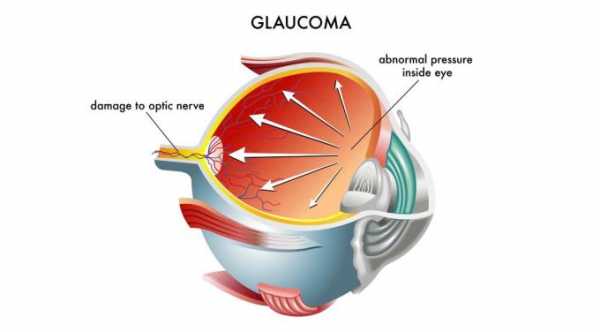
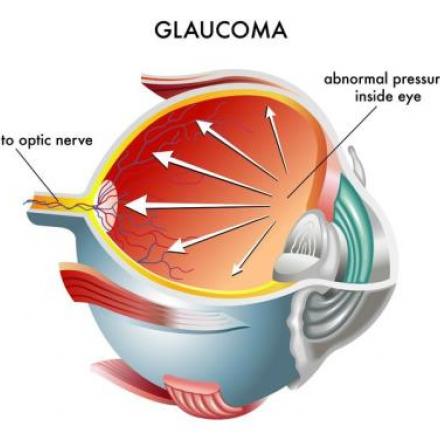
In eyes afflicted with Primary Open Angle Glaucoma, there is resistance to natural drainage of the eye fluids , causing an increase in the eye pressure. Most often, patients with drainage resistance also has a collapse of the Schlemm's canal.
Hydrus Microstent addresses these issues by dilating and scaffolding the Schlemm's canal to enhance the natural outflow of eye fluids.
Hydrus Microstent is developed by Ivantis, a company devoted in the development of glaucoma treatment.
On October 31, 2017, Ivantis announced that it has submitted the final Approval of Hydrus to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for market approval. It marks a significant milestone in making the Hydrus Microstent available in the market.
On November 13, 2017, Ivantis announced that its pivotal study has exceeded expectations. The study was conducted at 38 facilities in 9 different countries, involving 556 patients. It has been the largest randomized, controlled trial conducted for a MIGS device. The study was conducted to assess the safety and efficacy of Hydrus Microstent in lowering the IOP in glaucoma patients undergoing cataract surgery.
How does it work?
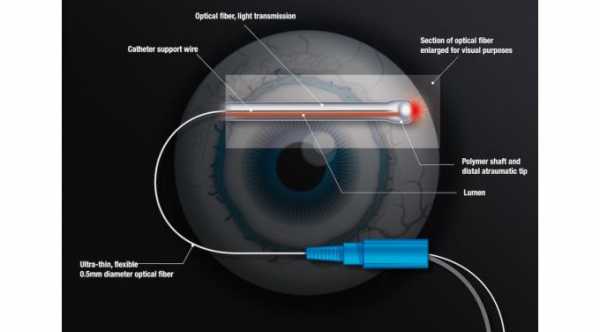
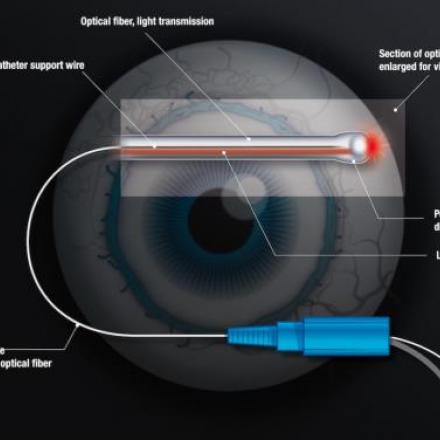
The Hydrus microstent is inserted into the primary fluid canal of the eye which is also called the Schlemm’s canal in order to dilate the channel and relieve obstruction of the eye fluid pathway. When the aqueous humor or the fluid inside the eye does not drain normally, the eye pressure increases. Allowing the blocked fluid to flow normally will treat the high eye pressure.
What is it made of?
The Hydrus microstent is made of a highly biocompatible alloy called nitinol which is composed of nickel and titanium. Nitinol is a super-elastic alloy with shape-memory. it remembers its original shape, and if the material is deformed it can return to its original shape once heated. Nitinol has been widely used in manufacturing medical implants for different body parts.
Hydrus is about the size of an eyelash. It is so minute that it won’t be seen or felt by the patient when implanted.
The Hydrus Procedure
The implant of Hydrus microstent is designed to be less invasive compared to traditional glaucoma surgery. It is inserted through similar methods as used in cataract surgeries and it can also be performed during a cataract surgery wherein the same incisions will be used.
The Hydrus cannula is inserted through the surgical incision in the cornea and directed across the eye positioning it near the Schlemm’s canal. Once properly positioned, the cannula engages the trabecular meshwork to guide the stent into the Schlemm’s canal.
The stent is then carefully advanced until the device fully exited the cannula. The cannula is then withdrawn from the trabecular meshwork and then out of the eye. The length of the stent covers 90 degrees of the Schlemm’s canal providing consistent access to the fluid channels in the eye.
It is a faster and safer procedure that may reduce the risks of complications with faster healing time than traditional glaucoma surgeries.