Ophthalmology Terminology P
Pachymetry. Measuring the thickness of the cornea.It is very important step in refractive surgeries.
Panretinal Photocoagulation. Using argon laser to treat or to burn the peripheral part of the retina in patients with diabetic retinopathy. The aims of this treatment is to decrease oxygen demand of the retina and to decrease secretion of angiogenic factors which induce the formation of abnormal retinal blood vessels.
Panum’s Space. Imaginary space in which any object inside this area will be seen singly while object outside this area will cause physiological double vision that will be suppressed physiologically by non-dominant eye
Panuveitis. Inflammation that involves all parts of the uvea which includes the iris, ciliary body and choroid.
Papilledema. Optic disc swelling that is caused by high intracranial pressure.
Papillitis. A form of Optic neuritis which involves only the optic disc.
Parinaud’s Syndrome. It is also called Dorsal midbrain syndrome. It occurs due to lesions to the dorsal midbrain such as in head injury , multiple sclerosis and arteriorvenous malformation.It has ocular manifestation such light near dissociation, lid retraction and convergence retraction nystagmus.
Pars Plana. Part of the ciliary body that face the vitreous body and lies close to the retina.Through this part, incision for vitrectomy surgery and intravitral injection is done. It lies about 4 mm from the limbus.
Pars Plana Vitrectomy. Ports for vitrectomy surgery are created in pars plana area of the eyes.
Pars Planitis. Inflammation that involves only the vitreous humor.It is the same as intermediate uveitis except that pars planitis is idiopathic or has no known causes and occurs mainly in children.
Penetrating Keratoplasty. A full thickness corneal surgery in which the damaged cornea of the patient is replaced by clear cornea. Another name of this procedure is corneal graft.
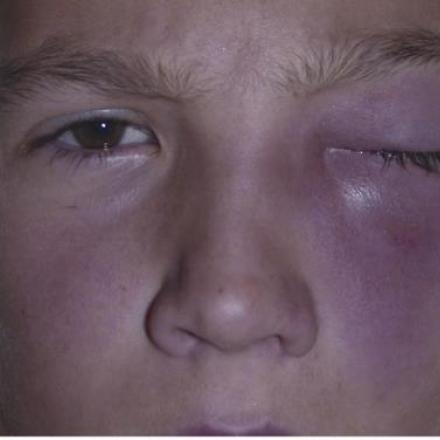
Periorbital Cellulitis.. Infection of the tissue the surrounds the eye globe and lies anterior or in front of the orbital septum of the eye. Once the infection penetrates this septum it is orbital cellulitis.
Peripheral Iridotomy. Procedure that is done either by laser or surgical tools. It creates a hole between the anterior and the posterior chamber of the eye which helps to decrease intraocular pressure.
Peripheral Ulcerative Keratitis. An Auto-immune disease with peripheral corneal thinning in the interpalpebral region of the eye. It occurs mainly in patients with connective tissue diseases such as Rheumatoid arthritis and Wegener Granulomatosis.
Peter’s Anomaly. Anomaly that occurs bilaterally with central corneal opacity and defects in the corneal stroma, descemet membrane and endothelium with a contact between cornea and lens or cornea and iris.
Phacomorphic Glaucoma
Phakic Intraocular Lens Implant
Phlebitis. Inflammation of the vein.
Photophobia. Excessive sensitivity to light.
Photopsia. The perception of sparks or flashes of lights.
Photorefractive Keratectomy. It is also called PRK. It is a form of refractive surgery in which the epithelial layer is removed and an argon fluoride excimer laser is used to ablate corneal stroma. It works well for patients with Myopia and Astigmatism.
Photostress Test. A special test for dark adaptaion that is used to evaluate the recovery time of photoreceptor to re-synthesize visual pigments.
Phthsis Bulbi. A condition which occurs as an end stage of chronic ocular diseases. It is non functional eye and characterized by small eye ball, disorganized ocular contents,calcification of the lens and retina,white cornea and low intraocular pressure.
Pierre Robin Sequence. It is a condition that presents at birth It can be associated with hereditary diseases such as Stickler Syndrome.
Pigment Dispersion Syndrome. Type of ocular disease which occurs mainly in adult, myopic and male patient. There is continuous rubbing of the back surface of the iris with the lens and zonules which lead to release of iris pigments into the aqueous humor. These pigments will deposit of the inner surface of the cornea, lens and trabecular meshwork. With time, the intraocular pressure can increase due to blockage of trabecular meshwork an din this case it is called pigment dispersion glaucoma.
Pinguecula. Benign growth of the conjunctiva. It has yellow white color and occurs mainly in the interpalpebral area of the area. It never invades the cornea which is how it can be differentiated from Pterygium which is the same thing but with corneal invasion.
Plauteau Iris Syndrome. A condition which occurs when there is anterior displacement of the ciliary body. This will cause narrow angle and can lead to angle closure glaucoma.
Pleomorphic Adenoma of Lacrimal Gland. A tumor that involves both parts of the lacrimal gland, orbital part and palpebral part. It is a benign tumor that occurs in the older patients with painless non-axial proptosis.
Pneumoretinopexy. Re-attachment of the detached retina through injection of Gas inside the eye. It has certain indications and can be done in outpatient.
Posner Schlossman Syndrome. Type of uveitis which is characterized by recurrent attacks of high intraocular pressure with corneal edema.
Posterior Blepharitis
Posterior Capsular Opacification
Posterior Capsule Rupture
Posterior Embryotoxon. A congenital condition with prominent and anteriorly displaced Schwalbe Line.
Posterior Keratoconus. Congenital condition in which the anterior or the front surface of the cornea is normal while the posterior or the back surface of the cornea has abnormal high curvature. Visual acuity is normal.
Posterior Polymorphous Corneal Dystrophy. Type of corneal dystrophy that affects the endothelial layer of the cornea. I t is bilateral disease that is presented at birth with bilateral diffuse corneal edema and vesicles.
Posterior Subcapsular Cataract. Type of cataract in which the opacity occurs in the back surface of the lens and beneath the capsule.
Posterior Vitreous Detachment
Potential Acuity Meter. A special test that can be used to test the visual acuity in patients with cataract and other media opacities by the projections of a miniature Snellen chart into the retina through a clear area of the cataract or opacity.
Pred Forte Eye Drops
Presbyopia. Inability to see objects at near because the natural lens loses its ability to reshape. It is a common condition that occurs around 40s.
Primary Acquired Melanosis, Conjunctiva. A condition that is characterized by proliferation of conjunctival epithelial melanocytes.It presents with flat pigmentation of the conjunctiva. It has the tendency to transform into infiltrating malignancy.
Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma. High intraocular pressure that occur due to closure at the angle of the eye. This closure occurs due to anatomical factors such as shallow anterior chamber and small eye and there are no associated ocular diseases. If there are causes for this closure other than anatomical factors, it will be called secondary angle closure glaucoma.
Primary Open Angle Glaucoma
Progressive Contact Lenses. Type of multifocal contact lenses.
Progressive Outer Retinal Necrosis. Necrosis of the retina that occurs in immunocompromised patients due to infection with Herpes Virus.
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Lesions in the retina with the formation of abnormal blood vessels and abnormal fibro-vascular membrane over the retina and optic disc due to Diabetes Mellitus.
Proptosis. Forward displacement of the eyeball.
Pseudoexfoliation Glaucoma
Pseudoptosis. A condition that simulates Ptosis.
Pterygium. Benign growth of the conjunctival tissue towards the cornea. Sometimes, it invades the cornea in which it can reach the center of it.
Ptosis
Punctal Plug. A small tool that is inserted in the punctum of the nasolacrimal duct to block it. It is used in patients with dry eyes to decrease the drianage of tears outside the eyes.
Punctuate Inner Choroidopathy. Idiopathic disease that affects young female patient.It affects the choroid and can cause the formation of choroidal neovascular membrane.
Pupillary Block
Purtschers Retinopathy. Retinopathy that is associated with severe trauma to the chest and head.